It doesn’t matter if you’re an established digital business or an up-and-coming online store looking to sell software, digital downloads, or digital content, a key part of selling online is making sure you’re familiar with how online payment processing works.
However, many businesses quickly realize that is easier said than done. Especially since there is a lot of technical jargon and terminology within the payment ecosystem. So much so that even just trying to figure out what to pay attention to can be overwhelming.
So, what is a payment gateway anyway? How are card payments validated? I’ve never even heard of a card association before!
The Key Players Involved in Online Payments
The sale of your software really involves four key components—a merchant, a customer, the payment gateway, and the payment processor. The technology connects the merchant and customer in the payment process.
-
Your customer, the buyer.
She’s super excited to get her hands on your product and can’t wait to see how the new digital good, software, or content will help her in her life. During checkout, she expects your website to adhere to proper PCI Compliance to ensure that you’re securely processing her payment information. Her issuing bank is responsible for approving the debit or credit card used in the transaction.
-
Your business, the digital goods provider.
For your business to accept debit and credit card purchases, you’ll probably need to partner with a merchant bank who’ll start accepting payments on your behalf. Your merchant bank (the acquirer) will also need to set up a merchant account for your business. You can think of this merchant account as the holding tank where all the funds from the sale of your products are held before being distributed into your company’s actual bank account.
It’s important to understand that merchant accounts can accept alternative payment options, but we’re focusing on just debit and credit card payments to keep things simple.
-
The Payment Gateway
Similar to the physical point of sale terminals found in brick and mortar stores, payment gateways act as a virtual terminal and allows businesses to accept debit and credit card payments directly from their site. There are regulations in place to protect the transmission of sensitive transaction data so payment gateways need to serve as the information highways for delivering encrypted payment information from an ecommerce site to the payment processor.
-
The Payment Processor
The payment processor is mainly responsible for connecting merchant accounts and payment gateways. After receiving the encrypted transaction data from the payment gateway, the payment processor runs the payment information through a card association—a network of issuing and acquiring banks that process payment cards—which will then authorize or deny the transaction request. This approval or rejection process will determine if the vendor is allowed to begin fulfilling the order.
The payment process may seem a little daunting at first. So we’re sharing a helpful infographic on navigating online payments for digital businesses.
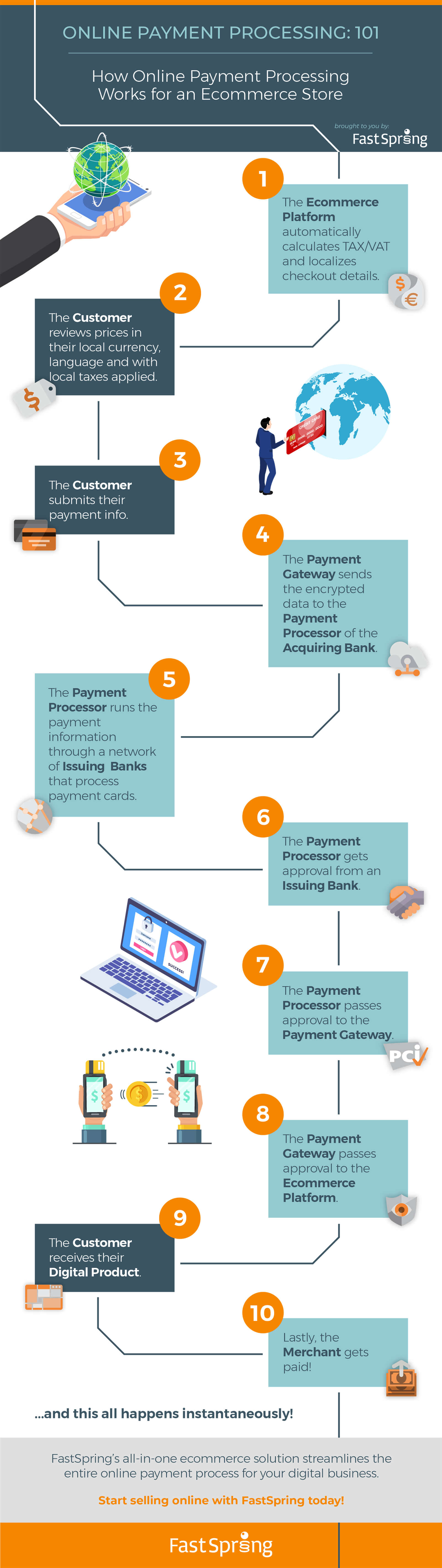
FastSpring Infographic: Online Payments for Digital Business
FastSpring as your Merchant of Record
FastSpring’s all-in-one ecommerce platform with global payment solution takes the hassle out of payment processing so you can focus on the rest of your business.
FastSpring’s easy-to-use platform does more than just ensure secure payment processing. As your Merchant of Record, FastSpring assumes all financial liability for your business. This includes chargebacks initiated by your customers, declines, and other back-office operations for your ecommerce business. Merchants of Records, like FastSpring, even help you stay compliant with local and international laws by handling VAT and taxes on your behalf.
Is your business ready to start accepting online payments and grow sales volume? Click here to download our guide: What You Need to Know About Selling Online.